Introduction
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) research has been steadily growing, bringing with it a significant increase in energy consumption. Traditional digital chips used for AI models are in short supply worldwide, leading researchers to explore alternative solutions. One such solution is the use of analogue chips, which have the potential to run AI models more efficiently and reduce energy consumption. IBM Research has developed an analogue chip that can significantly improve AI efficiency and reduce bottlenecks in AI development.
The Energy Challenge
The energy use of AI has rapidly grown, with studies showing a 100-fold increase from 2012 to 2021. This rise in energy consumption is largely powered by fossil fuels, leading to concerns about the long-term sustainability of AI research. To compound the issue, there is a global shortage of digital chips, particularly the graphic processors (GPU chips) that are commonly used for training and running AI models. This shortage has resulted in increased demand and limited supply, causing delays in AI research and development.
The Benefits of Analogue Chips
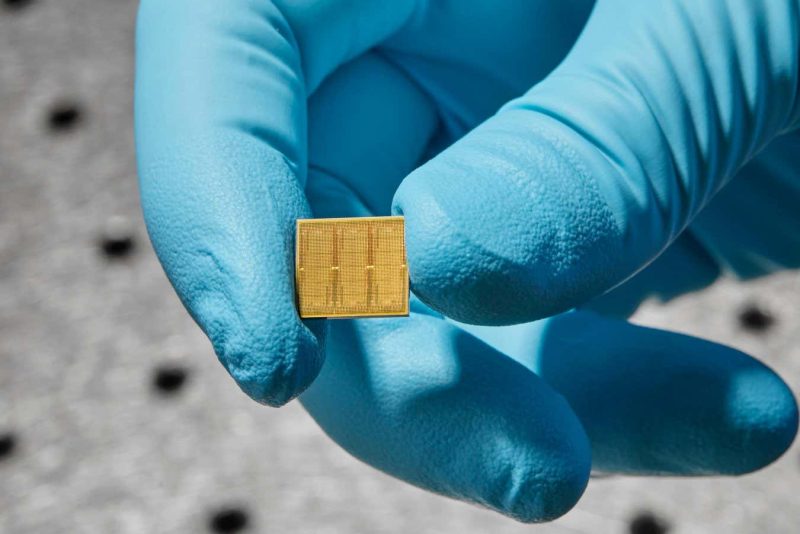
One of the main drawbacks of current AI hardware is the need to shuttle data back and forth between memory and processors, leading to significant bottlenecks. Analogue compute-in-memory (CiM) chips offer a potential solution to this problem. These chips can perform calculations directly within their own memory, minimizing data transfer. IBM’s analogue chip contains millions of phase-change memory cells that can represent the synaptic weights between artificial neurons. This allows the chip to store and process these weights without the need for multiple operations to recall or store data in distant memory chips.
Efficiency and Future Potential
In tests on speech recognition tasks, IBM’s analogue chip demonstrated an efficiency of 12.4 trillion operations per second per watt. This is up to 14 times more efficient than conventional processors. While the chip is still in the early stages of development, experiments have shown its effectiveness with commonly used AI neural networks. The chip has the potential to support popular applications such as ChatGPT.
Limitations and Future Considerations
While highly customized chips like the analogue chip provide unparalleled efficiency, there are limitations to their functionality. Just as a GPU cannot perform all tasks that a CPU can, the analogue chip has its own limitations. However, if the trend of AI research continues, highly customized chips like the analogue chip could become more common. The chip, although specialized, can be potentially repurposed for other AI tasks beyond speech recognition, providing value and reducing electronic waste.
Conclusion
By replacing traditional digital chips with analogue compute-in-memory chips, researchers aim to reduce the energy consumption associated with AI models. IBM’s analogue chip has shown promising results in terms of efficiency and has the potential to alleviate bottlenecks in AI development. Although still in the early stages, these chips could offer a more sustainable and efficient solution for the growing energy demands of AI research.