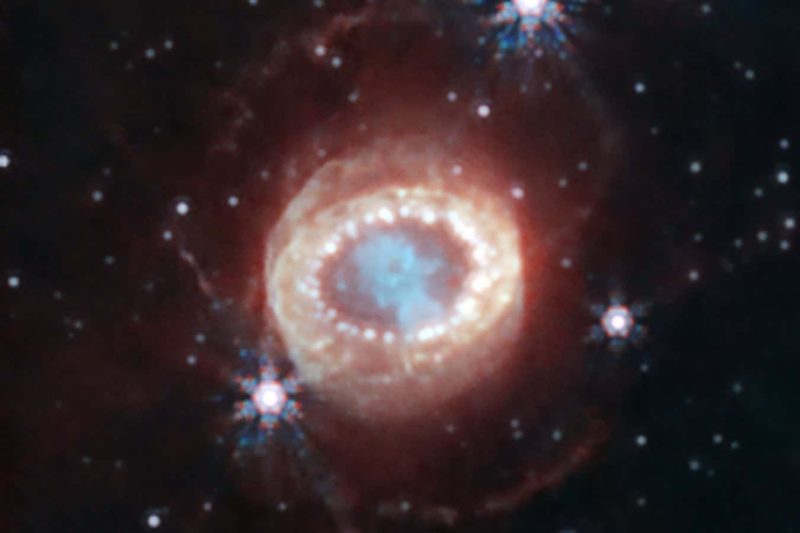
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured a new image of one of the universe’s most famous supernovae, SN 1987A, providing astronomers with a closer look at its structure and evolution. SN 1987A is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud and was first observed in 1987, making it the nearest stellar explosion since Kepler’s supernova in 1604. Over the years, astronomers have extensively studied the remnants of SN 1987A, and JWST’s observation offers unique insights.
Unveiling the Supernova
Using infrared light, the JWST’s image showcases the intricate details of SN 1987A. The central blue region represents dense clumps of gas and dust that were expelled during the explosion. Surrounding the blue region is a previously unseen crescent-like structure in red, which is likely an outer layer of hydrogen gas ejected from the supernova. Additionally, a bright ring of matter encircles the blue area and the crescent, formed from material expelled by the original star in the thousands of years leading up to the explosion.
Missing Neutron Star
Typically, a supernova explosion results in the formation of a neutron star. However, despite extensive observations, astronomers have not yet detected a neutron star in SN 1987A. Mikako Matsuura, a researcher from Cardiff University, suggests that the gas and dust within the system may be absorbing the light emitted by the neutron star, making it difficult to observe.
Continued Monitoring
Matsuura and her team plan to continue monitoring SN 1987A with the JWST. The supernova provides a unique opportunity to study the evolution of supernovae over time and holds valuable insights into their behavior.
Key Takeaways:
- The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured a detailed image of the supernova SN 1987A.
- The image reveals a blue central region of dense gas and dust, a red crescent-like structure, and a bright ring of matter.
- Astronomers have not yet located a neutron star, which is typically formed after a supernova.
- Continued monitoring of SN 1987A will provide insight into the evolution of supernovae.