Topics:
- The James Webb Space Telescope’s Discovery
- Composition of Early Stars
- The Significance of GLASS-z12
- Carbon-to-Oxygen Ratio
- Mysteries of Population III Stars
- Future Observations and Implications
The Significance of the Discovery
The James Webb Space Telescope has potentially captured the remnants of the universe’s earliest supernovae, shedding light on the chemical traces left by the first stars. These population III stars, formed shortly after the big bang, played a crucial role in the creation of heavier elements fundamental to our existence.
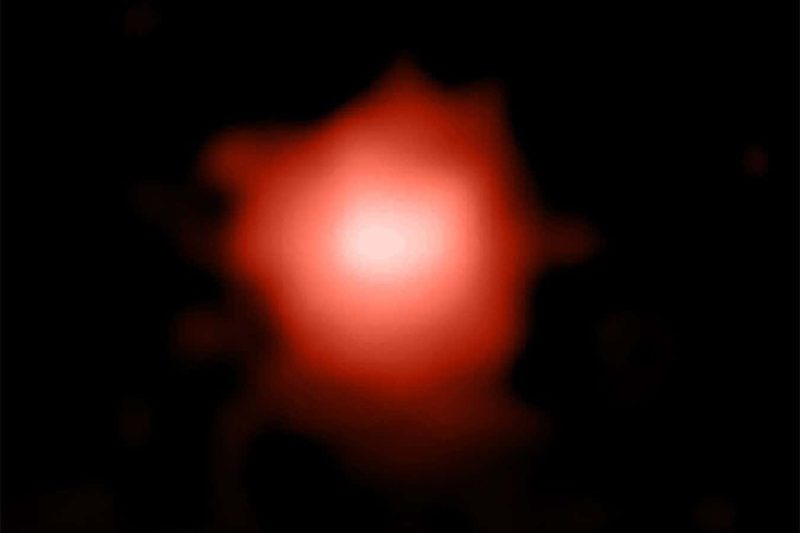
The galaxy GLASS-z12 shows signs of the earliest supernovae in the universe
Naidu et al, P. Oesch, T. Treu, GLASS-JWST, NASA/CSA/ESA/STScI
Insights from GLASS-z12
The study of the galaxy GLASS-z12, born just 350 million years after the big bang, has revealed the presence of carbon along with weaker detections of elements like oxygen and neon, marking it as the most distant source of heavy elements in the universe. This finding provides valuable insights into the early cosmic processes and the formation of essential elements.
Carbon-to-Oxygen Ratio Mystery
An intriguing observation in GLASS-z12 is its higher carbon-to-oxygen ratio compared to newer galaxies. This disparity poses a challenge in understanding the mechanisms responsible for the abundant carbon in this ancient galaxy, ultimately pointing towards the unique characteristics of population III stars and their potential role in the universe’s elemental evolution.
Unraveling Population III Stars
Population III stars, characterized by their low-energy nature and high purity in hydrogen and helium, are speculated to be the source of the observed carbon abundance. The enigmatic nature of these early stars and their distinct supernova events prompts further exploration into their contribution to the universal elemental enrichment.
Future Prospects and Implications
While delving deeper into the complexities of GLASS-z12 presents challenges due to resource constraints, the pursuit of similar ancient galaxies and comprehensive carbon ratio measurements holds the key to unraveling the mysteries surrounding population III stars and their profound impact on cosmic evolution.
Experts’ Views and Speculations
Experts express surprise at the detection of high carbon levels in such an ancient galaxy, while acknowledging the need for further investigations to validate the role of population III stars in shaping the early universe. The uncertainties surrounding population III supernovae and their distinct characteristics present a compelling avenue for future astronomical endeavors.