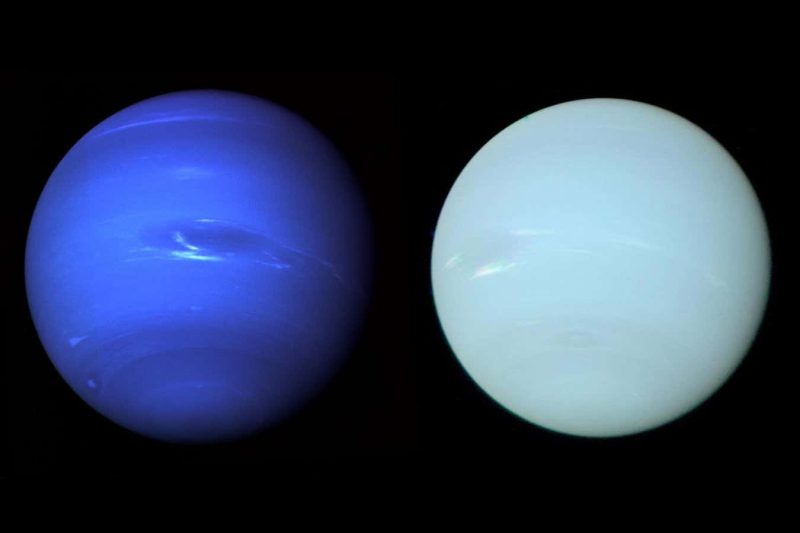
The unique Voyager 2 picture of Neptune (left) and the reprocessed picture from the brand new examine (proper)
Patrick Irwin
Neptune’s true color is a pale greenish-blue just like that of Uranus, opposite to fashionable pictures that present it to be a a lot deeper shade of blue.
NASA’s Voyager 2 spacecraft flew previous the outer planets within the Nineteen Eighties and despatched again pictures displaying that Uranus and Neptune had been markedly completely different colors.
That is puzzling, given their related measurement, mass and chemical make-up. Fashions of the planets’ atmospheres can clarify a few of the variation – corresponding to a “haze layer” that’s thicker on Uranus and displays extra white gentle, making the planet seem lighter – however these don’t absolutely clarify why the planets ought to have such completely different hues.
Now, Patrick Irwin on the College of Oxford and his colleagues have processed the Voyager 2 pictures to indicate how the human eye may see the planets.
The unique pictures of Neptune taken by Voyager 2 had an enhanced distinction ratio to spotlight hard-to-see atmospheric options. Together with the way in which that the colors had been balanced to make a remaining composite picture, this made the planet seem bluer.
Scientists on the time knew this and included these modifications in image captions, however over time the captions had been separated from the pictures and Neptune’s deep blue shade grew to become enshrined as reality within the public consciousness, says Irwin.
Photographs of Uranus (left) and Neptune (proper) produced beforehand and within the new examine
Patrick Irwin
He and his workforce developed a mannequin to transform the uncooked picture information to a true-colour picture utilizing photographs taken by the Hubble Area Telescope, which include extra full details about the sunshine. This produced related shades for each planets. “The true-colour picture is way more boring and bland due to the way in which the attention works,” says Irwin.
The researchers additionally used the Hubble pictures, together with pictures from Lowell Observatory in Arizona, to construct a mannequin that predicts how Uranus’s color modifications throughout its lengthy, 84-year orbit across the solar. Due to the planet’s spin, we see extra of the equator throughout the equinoxes and extra of the poles throughout the solstices. On the equator, there’s extra methane, which absorbs crimson gentle. The planet additionally has a hood of reflective, brightening ice particles that types on the sun-facing pole throughout the equinoxes, growing the reflectivity of crimson and inexperienced wavelengths.
This helps clarify the long-standing thriller of why Uranus seems barely greener in its solstices. “We knew there was a hood, and we knew there’s much less methane on the poles, however nobody had put all of it collectively to elucidate what’s really occurring seasonally,” says Irwin.
Subjects: