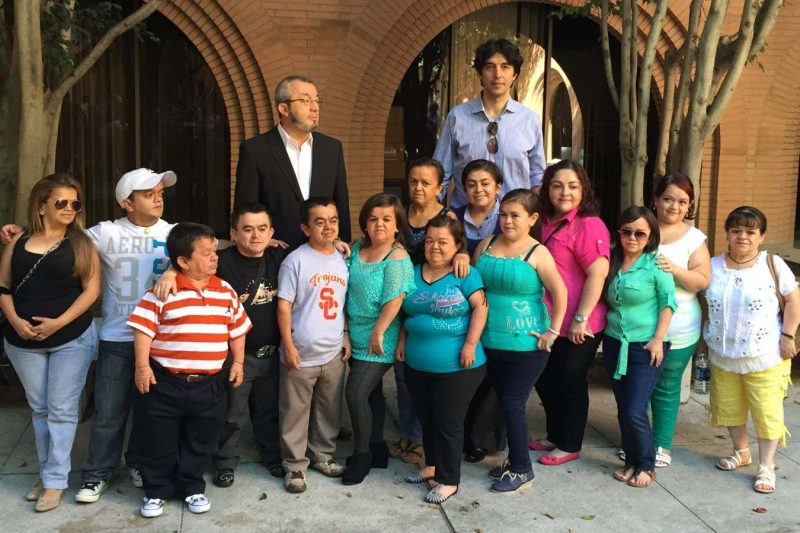
Two of the researchers with a number of of the research members, who’ve Laron syndrome
Jaime Guevara-Aguirre and Valter Longo
Individuals with a uncommon genetic mutation that causes brief stature and may make them dwell longer are serving to make clear the causes of ageing.
These with the bizarre gene variant have a number of traits that shield towards coronary heart illness, one of the crucial widespread causes of demise, which can clarify why their life expectancy exceeds that of the overall inhabitants.
A signalling molecule referred to as insulin-like development factor-1 (IGF-1) has lengthy been suspected to play a job in longevity. A number of animals, comparable to worms and mice, have been discovered to dwell longer if their ranges of this compound are lowered artificially, comparable to by genetic modification. Centenarians also have slightly lower levels of IGF-1, on common.
In most species, IGF-1 promotes development when animals are younger and in later life impacts how cells use vitality. One thought is that there’s a trade-off between animals investing their vitality in additional development or well being upkeep.
“If you develop previous and also you begin breaking down, you don’t need to spend vitality on development, you need to spend vitality on stopping your breakdown,” says Nir Barzilai on the Albert Einstein School of Medication in New York, who wasn’t concerned within the new analysis.
The query of whether or not the trade-off additionally occurs in individuals will be studied through a uncommon genetic situation referred to as Laron syndrome, which was first recognized in a bunch of Ecuadorian individuals whose ancestors left Spain in the course of the Inquisition a number of centuries in the past.
The mutation causes individuals to have a defective receptor for development hormone, main them to be brief in stature. Individuals with Laron syndrome even have decrease ranges of IGF-1, as a result of launch of this compound is often triggered by development hormone.
As a result of there are so few individuals with the mutation, it’s unclear whether or not they do certainly have longer lifespans. Suggestive evidence came from a 2011 study of 90 Ecuadorian people with Laron syndrome, which impacts an estimated 400 to 500 individuals worldwide.
This discovered there have been extra individuals with the situation who had been surviving for longer than anticipated, in contrast with the overall Ecuadorian inhabitants. “We all know that they’re over-represented at older ages,” says Valter Longo on the College of Southern California in Los Angeles.
Within the newest research, Longo and his colleagues in contrast 24 individuals with Laron syndrome, both from Ecuador or the US, with 27 of their family members who lacked the mutation. These with Laron syndrome appeared more healthy on a number of heart-related measures, together with blood stress, blood sugar ranges and sensitivity to the hormone insulin, which is concerned in blood sugar management.
Individuals with the mutation additionally had increased ranges of a compound referred to as low-density lipoprotein, often known as “dangerous ldl cholesterol” as it’s thought to predispose individuals to artery plaques that may result in coronary heart assaults. However solely 7 per cent of the individuals with Laron syndrome had such plaques, in contrast with 36 per cent of their family members.
Whereas the small variety of individuals within the research meant this distinction might have arisen by probability, it suggests their arteries seem no unhealthier than these of individuals with out the mutation, says Longo.
It has additionally beforehand been proven that individuals with Laron syndrome are much less prone to develop most cancers and will have much less of the cognitive decline that normally happens at older ages.
The brand new discovering helps the concept by some means dampening IGF-1 signalling pathways in later life might sluggish the ageing course of, says Alexei Maklakov on the College of East Anglia in Norwich, UK. “It’s a query of timing,” he says. “You undoubtedly don’t need to do it throughout vital levels of development and growth. However later in life, you might presumably intervene with the operate of those pathways.”
Matters: