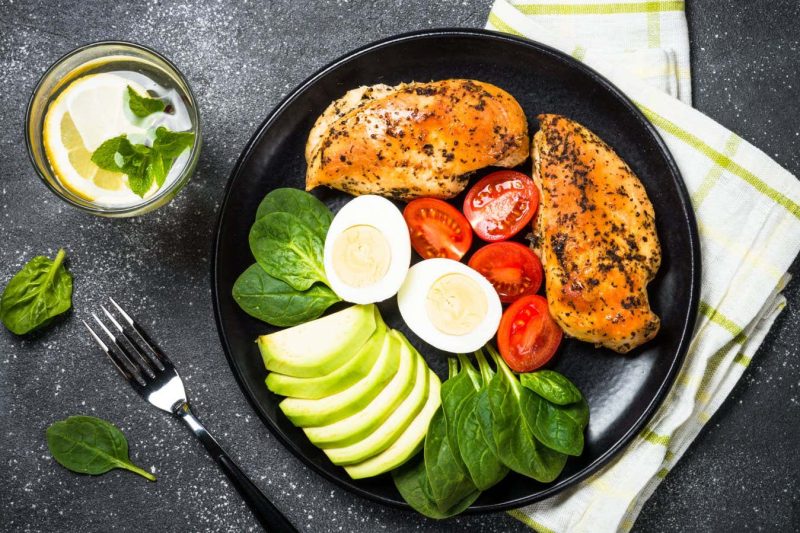
Analysis on the well being results of low-carbohydrate diets like keto has had blended outcomes
nadianb/Shutterstock
A ketogenic food regimen causes broken cells to build up within the organs of mice. Their build-up suggests the keto food regimen might speed up organ ageing, elevating the danger of circumstances like coronary heart illness and most cancers.
Though many individuals have adopted low-carbohydrate diets like keto for weight reduction and controlling blood sugar, analysis on their well being results is blended, with some research discovering they improve the danger of coronary heart assaults.
To study extra, David Gius on the College of Texas Well being Science Middle at San Antonio and his colleagues fed six mice a ketogenic food regimen for 3 weeks. Greater than 90 per cent of their energy got here from fats and fewer than 1 per cent from carbohydrates. A management group ate an ordinary food regimen the place 17 per cent of energy got here from fats and 58 per cent got here from carbohydrates.
The researchers then analysed coronary heart, kidney, liver and mind tissue samples from the mice, in search of senescent cells. Senescence happens when cells turn out to be too broken to perform, however as a substitute of dying, they enter a zombie-like state. These cells linger in tissues, spewing toxins that stoke irritation.
Animals on the ketogenic food regimen had considerably extra senescent cells of their organs in contrast with these on an ordinary food regimen. For example, their kidneys contained, on common, 4 instances the quantity of a marker of mobile senescence as these from animals fed a daily food regimen.
Senescent cells improve with age. So, these findings counsel the keto food regimen would possibly speed up organ ageing, which might elevate the danger of circumstances like coronary heart illness, most cancers and sort 2 diabetes. Nonetheless, switching mice again to an ordinary food regimen decreased senescent cells.
“Whereas the ketogenic food regimen might be a very good factor, [it is not for] everybody. And importantly, you have to take a break,” says Gius. “I feel our paper actually says we have to examine this extra rigorously.”
It isn’t clear how these experimental findings might translate to individuals, says Russell Jones on the Van Andel Institute in Michigan. “They’re working a 90 per cent fats food regimen, and that may be just about not possible to stick to as a human,” he says.
Subjects: